Welcome
Beginner GIT Cheat sheet
Imagine working on a project and accidentally deleting important code. Or collaborating with teammates, only to have conflicting changes overwrite each other. Git solves these problems by tracking every change you make to your code—like a time machine for your projects.
Git is version control software. It records what changed, who changed it, and when. Whether you’re building solo or with a team, Git lets you work confidently, knowing you can always revert to a previous version if something breaks.
Git has dozens of commands, but beginners only need 10–15.
Download links at the bottom of the page.

Download links:
Name/Size: GIT_Cheatsheet.pdf/27KiB
SHA256: 369efbf9d56e36a1abb2bd79085d498ae1c713b26079a21e5e286de3200ba579
How plan, test, and validate Microsoft 365 environments?
Before rolling out large-scale desktop changes, IT teams benefit from an isolated environment to validate workflows without impacting users. The Microsoft 365 deployment lab kit provides that sandbox, enabling hands-on testing of OS deployment, configuration, security, and cloud management paths.
The lab includes evaluation builds of key tools such as Configuration Manager and supports optional integration with Intune for hybrid (on-prem + cloud) scenarios. You can test deployment methods like task sequences and Autopilot to simulate device enrollment and provisioning.
For engineers using virtualization, the environment can be hosted on Hyper-V, making setup rapid, repeatable, and disposable.
Reserve 30–60 minutes to deploy and run this lab prior to production rollout. The upfront validation reduces risk, increases deployment confidence, and accelerates readiness for a modern workplace model.
Its free and available to download here.

Brave
Brave Browser offers a refreshingly simple vision of what the web could be: a place where the user, not the advertiser,comes first. From the moment you open it, Brave removes much of the clutter that has come to define the modern browsing experience: third-party ads, trackers, pop-ups and intrusive banners vanish, leaving pages to load far quicker and with less distraction.
Under the hood, Brave quietly strengthens your privacy by blocking tracking cookies, shielding you from fingerprinting, and upgrading connections to HTTPS whenever possible. It’s like giving your browsing a protective filter, with no extra setup required.
But Brave doesn’t ask you to give up convenience. It remains compatible with familiar extensions, syncs across devices, and — for those who care — offers its own independent search engine that doesn’t build a profile on you. For users curious about cryptocurrencies, it even includes a crypto wallet and support for the Basic Attention Token (BAT), enabling a more user-centric–and optional–way of supporting content creators.
In essence, Brave reimagines the web: clean, fast, private—and firmly under your control. It’s a quiet rebellion against tracking, bloat and noise, built with the hope of putting the web back into the hands of people. It free and available to download here.

Visual Studio Code
Visual Studio Code, often called VS Code, is one of the most popular code editors used by developers today. One of the best things about VS Code is how lightweight it is. It opens quickly and doesn’t slow down your computer.
VS Code has extensions, you can easily add for any programming language, such as Python, JavaScript, or C++. You can also install themes, code formatters, and even AI tools like GitHub Copilot.
When you start typing code, VS Code gives you smart suggestions through a feature called IntelliSense, a built-in debugger, so you can run your programs and fix errors without leaving the editor and built-in Git integration.
VS Code works on Windows, macOS, and Linux. You can even use it online through VS Code for the Web, so your coding environment can go wherever you do. It’s free, fast, and filled with smart tools that make coding easier for everyone, from beginners to experts. It can be downloaded here.

endoflife.date
The website endoflife.date is a simple, reliable website that tracks end-of-life dates for software, programming languages, operating systems, and more. It helps developers, IT teams, and organizations plan upgrades, avoid security risks, and stay informed — all in one easy-to-browse place. It’s important because using software past its end-of-life puts systems at risk by missing critical security updates and support.
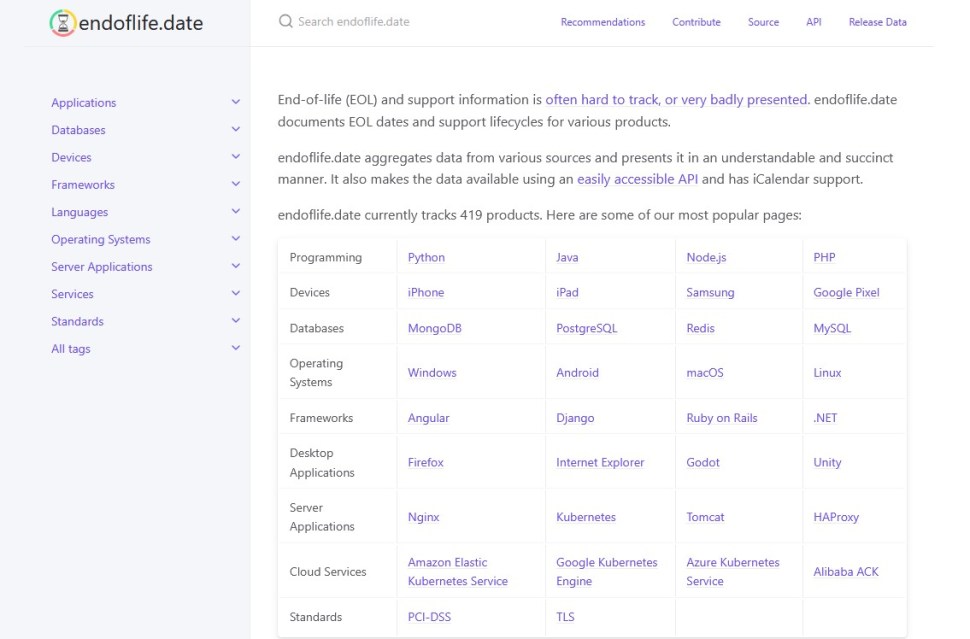
URL: endoflife.date
GIT
GIT is a version control system that tracks changes to files, created by Linus Torvalds for the development of the Linux kernel. It lets you save versions, go back if something breaks, and work with others without overwriting each other’s work.
Git has simple commands like git add, git commit, and git push. It’s the backbone of tools like GitHub and is essential for developers and DevOps teams.
The application is free, compatible with multiple operating system and can be downloaded here.

github.com
GitHub is a cloud-based platform that helps you store, track, and collaborate on code using a tool called Git. It’s widely used by developers, DevOps engineers, and IT teams to manage projects, automate workflows, and work together more efficiently.
With GitHub, every change to your code is tracked, so you can go back, compare versions, or fix mistakes easily. It also makes teamwork easy—multiple people can work on the same project without overwriting each other’s changes, using branches and pull requests.
Getting started is simple: create an account on github.com, install Git, and create a repository to begin tracking your work.
Whether you’re automating scripts or building full applications, GitHub is an essential tool in modern IT and DevOps.

URL: github.com
Use the IT skills you already have to transition to DevOps
Breaking into DevOps from another IT role can feel like entering a whole new world, with a whole new language, full of pipelines, YAML, and unfamiliar tools. But the truth is, you’re already halfway there.
If you’ve worked in IT support, system administration or as a network engineer, you’ve already built some core skills like automation, troubleshooting, and cross-team communication.

Your days were already filled with diagnosing and solving problems, often with limited context. Whether it’s a broken login, a DNS issue, monitoring VMs or a printer rollout, very likely you have seen been the project manager, implementer and QA.
Have you ever written a PowerShell script to automate user onboarding? A Bash script to reboot a server fleet? Or a quick Batch script to maps things and distribute it as a GPO? That’s automation, hence that’s DevOps.
A good DevOps engineer understands systems from the ground up. You’ve already been tracking system health, uptime, disk usage, and more. Your knowledge of operating systems, networking, user roles, and permissions is invaluable.
The move from another frontline IT role to DevOps builds on what you already know, such as system insight, problem-solving, and scripting are solid foundations.
6 years!
Marking the 6 years of the blog!

HCP Packer
HashiCorp Packer is a tool used to automate the creation of identical machine and container images across multiple platforms.
By using a single source configuration, Packer streamlines the process of building system images, ensuring efficiency and consistency. It supports multiple cloud providers and private infrastructure, allowing users to create images for various platforms in one go.
Packer is highly extensible, enabling users to add plugins for builders, provisioners, post-processors, and data sources. It is commonly used for automating image builds, managing “golden images,” ensuring image compliance, and integrating with other HashiCorp tools like Terraform.

HCP Terraform
Terraform revolutionizes the way we manage infrastructure. By adopting Terraform and embracing Infrastructure as Code, organizations can simplify and automate the process of provisioning resources, improve collaboration, and ensure security and compliance across their infrastructure.
Through the adoption, building, standardization, and scaling of Terraform workflows, teams can operate more efficiently, manage costs effectively, and meet the ever-growing demands of modern cloud environments. Terraform’s flexibility and power allow organizations to extend these practices across their entire infrastructure ecosystem, from development to production.
If you’re looking to modernize your infrastructure management and embrace IaC, Terraform is a powerful tool to help you get there—providing the scalability, automation, and collaboration needed to thrive in today’s cloud-native world.
More information can be found here.

az-vm-image.info
This web site becomes very useful when you want to share a list of available operating system images for Azure VMs to a project manager that doesn’t have Azure CLI installed.







